In this blog post, we will be explaining what a PEP screening is and giving you the main points you need to be educated about. PEP screening is used for eliminating risks like money laundering and other financial crimes by identifying and monitoring people who are known as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs). There are several types of PEPs to learn about. First is domestic PEPs; these people are operating within the same country. Some examples we can give is government officials, members of the judiciary, or executives within state-owned enterprises. The second type is foreign PEPs; these people are from another country. Examples for foreign PEPs are high-ranking government officials, diplomats, or executives holding significant positions in international organizations. Lastly, international organization PEPs are people who are senior management of organizations like the UN, World Bank, and IMF.
There are several high-risk roles that require PEP screening, some of which are heads of state, senior government officials, high-ranking military officers, members of parliament, and executives of state-owned enterprises.
What is PEP Screening?
PEP check (screening) is an essential element of AML (Anti-Money Laundering) compliance and it enables institutions to identify and monitor if your client is Policitally Exposed Person, see the risk factors, you can apply EDD if required.
What is the Role of PEP Screening in AML Compliance?
PEP screening helps immensely with AML compliance since PEPs are high-risk customers. The reason for PEPs being high-risk customers is because of their potential abuse of power caused by their high-ranking job positions. PEP screening is also important since it is a FATF recommendation 12 requirement; being in compliance with FATF recommendations is essential. Finally, PEP screening is needed because it helps prevent bribery, corruption, and laundering of public funds.
Why Does PEP Screening Matter?
PEP screening is crucial in helping companies meet regulatory obligations; AML and KYC compliance is really important for companies. It also helps the company protect its reputation as well as reducing enforcement risks. AIA Group Ltd. was fined HK$23 million since the firm’s AML screening technology failed to flag most Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs); this led to delayed identification of the sources of their wealth and funds.
Why is PEP Screening Required?
We’ve mentioned before that PEP screning is important since it helps companies reach their regulatory obligation goals. Regulatory bodies like AMLD in the EU, FinCEN in the U.S., MAS in Singapore, and many more require AML and KYC compliance. PEP screening helps meet these requirements. Using a risk-based approach (RBA) demands PEP screening along with it. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is needed for high-risk PEPs. Along with this, ongoing monitoring of PEPs is any requirement set forth by regulatory bodies and it helps companies with their compliance goals.
What Is PEP Screening Software?
We’ve established that PEP screening is needed when reaching AML and KYC compliance is your goal, but doing this manually will take a lot of time. PEP screening software is the compliance tool that helps with this problem. The PEP screening software automatically identifies and then monitors PEPs during processes like onboarding and doesn’t stop afterwards; the ongoing transactions are also monitored. It helps companies meet AML/KYC regulations by identifying high-risk individuals who might deal with money laundering or other financial crimes before it gets too late.
The PEP screening software achieves this by checking several PEP lists worldwide. By doing this, it ensures that organizations detect risky people early on. There are several benefits to automating this process. First of which is real time detection of high-risk clients; this helps you figure out who has the potential of committing crimes and needs to be monitored quickly. Another benefit of automating the process is audit trails. By keeping records of past checks, it helps support regulatory reporting and will be helpful in case of internal investigations. Finally, automating menas that you can speed up and widen your search scale without needing much labor or time.
How Does PEP Screening Software Work?
PEP screening software operates by first watchlist making. This means that the customer’s details are checked using fuzzy logic; this is done to catch spelling variations, aliases, and translations of the same name. The second thing it does is risk scoring and alert generation. What we mean by this is that each match we previously got gets evaulated with a risk score; after this is done, alerts are done tfor the potential high-risk people. Finally, case management and documentation is done. Compliance teams can review these alerts previously achieved, report these cases and then save them in case of a later need; this ensures regulatory requirements are met.
Top PEP Monitoring Software Providers in 2025
There are several PEP monitoring software providers that can help you meet your AML/KYC compliance goals. Some of which are Sanction Scanner, ComplyAdvantage, Dow Jones Risk & Compliance, Refinitiv World-Check, and LexisNexis Bridger Insight.
Sanction Scanner is perfect for those who are looking for an all-inclusive AML solution for their problems. Fintech companies, cryptocurrency firms, and banks can benefir greatly from their real-time monitoring.
ComplyAdvantage is for those who are at the beginning stages of their compliance journey. This provider is powered by machine learning.
Dow Jones Risk & Compliance is recommended for those who are looking for a tool that uses manually validated data; it is for you if you are a global finance institiution with high compliance requirements.
Refinitiv World-Check for banks that have substantial compliance budgets as well as traditional infrastructure. High-risk entities can get flagged and later original risk notes are given to the bank.
LexisNexis Bridger Insight is popular with insurance and lending sectors. Sadly, its interface is not really accessible. You can get PEP screening from this provider as well.
| Provider | ID verification |
| Sanction Scanner | Real-time global database, customizable risk scoring, API-first structure |
| ComplyAdvantage | Advanced AI-driven screening |
| Dow Jones Risk & Compliance | Rich and curated PEP list |
| Refinitiv World-Check | Sanction lists with strong analyst curation |
| LexisNexis Bridger Insight | Robust due diligence tools |
| NameScan | Affordable, easy-to-integrate screening |
| Shufti Pro | ID verification |
What to Consider When Choosing a PEP Monitoring Tool
There are several things you need to consider and keep in mind when choosing a PEP montioring tool. The first thing to consider is getting real-time updates, this helps greatly with compliance. Global database coverage is another item on our list that will help you immensely; having wider coverage will make sure you are getting the best results. Another thing that can benefit you greatly is API integration. Integrating your already existing systems will make sure you are reducing manual work. Fuzzy matching quality is another item that our readers need to be careful about; your tool being able to detect variations, aliases, and translations is a must.
Finally, cost effectiveness is our final item to consider when choosing a PEP monitoring tool. Make sure you are getting the best service with its adequate pricing.
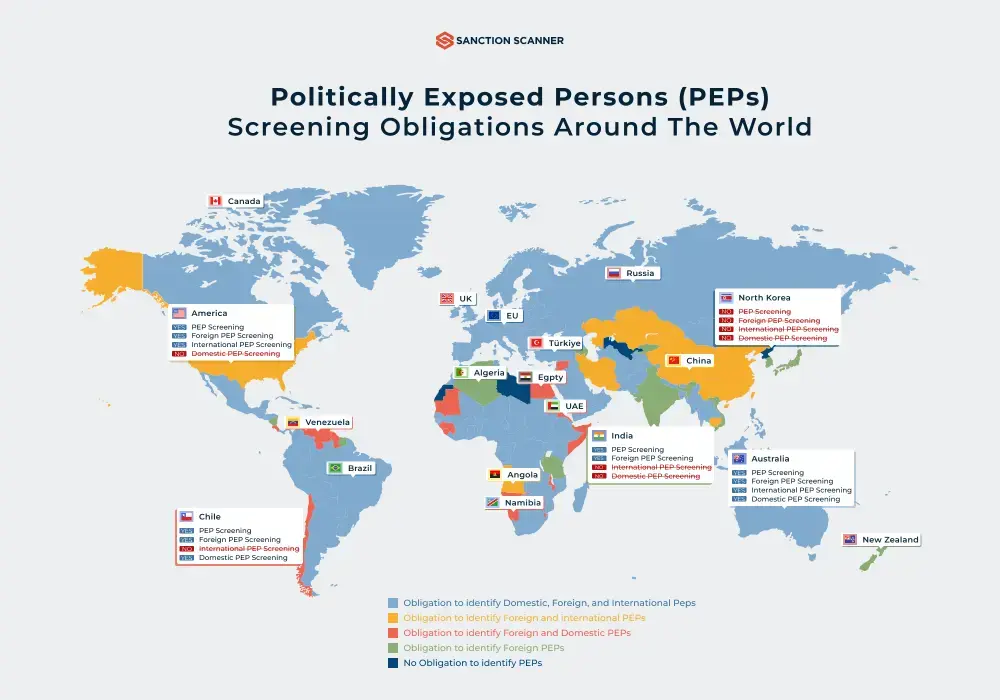
PEP Screening Requirements by Country
FinCEN of the U.S. requires Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for foreign PEPs, this includes things like ongoing monitoring and risk assessment. Another regulatory body is AMLD of the EU; this regulatory body requires ongoing due diligence for PEPs, and covers both domestic and foreign PEPs.
Our third regulatory body is MLRs 2017 of United Kingdom, which demands risk based EDD for both domestic and foreign PEPs. One other regulatory we can mention is FINTRAC of Canada; it demands identification of family members and close associates of PEPs.
Another regulatory body is AUSTRAC of Australia; it requires risk-based obligations, which ensures controls according to PEP risk levels. One other regulatory body is MAS of Singapore, which requires group-wide controls for all branches and affiliates. Our seventh regulatory body is CBUAE guidance of UAE, it demands this guidance on PEP onboarding to help with risk assessment. One other regulatory body is FSA of Japan, this institution focuses on its monitoring criteria, risk profiling and periodic checks are needed. Another regulatory body is RBI/SEBI of India; it requires EDD for PEPs. Finally, COAF of Brazil requires its enhanced scrutiny of PEPs as well as ongoing monitoring, reporting suspicious activities and more.
What Are the Common Techniques Used in PEP Screening?
The first common technique used in PEP screening is fuzzy matching. This helps you prevent getting false positives because of variations, aliases, and translations. Another thing that helps greatly is ongoing monitoring. Since you need to be able to up-to-date with your data regarding PEPs, ongoing monitoring is essential.
Finally, adverse media screening is another technique used in PEP screening. Adverse media screening is used to determine the negative news or the lack thereof about PEPs by researching global sources
Automated vs Manual Screening
In this part, we’ll discuss the differences between automated and manual screening. Automation gives you faster results. It achieves this while handling a large scale of records efficiently without needing more labor. It uses features like fuzzy logic as we mentioned above, and features like these help improve accuracy. Whereas with manual screening, you may need its help more with complex or ambigious cases. It helps provide more context to these situations. Once a risk is confirmed, it helps escalate them to compliance officers.
What is Included in a PEP Check?
When you decide to get a PEP check, the first thing included is identity and role verification. To make sure this person is who they say they are, these information being checked is essential. The second measure taken is finding out this person’s relationship to government or public functions. Finally, widening this search to include family members and close associates is really helpful. This additional screening makes sure you miss nothing during the process.
What are the PEP Screening Requirements by Country?
Like we mentioned above, PEP screening requirements are different for different regions. In the U.S. where FinCEN is the regulatory body, financial institutions must apply EDD for foreign PEPs. AMLD for the EU and MLRs 2017 for the UK require ongoing, risk-based due diligence for both domestic and foreign PEPs; while FINTRAC of Canada needs identifying of family members and close associates. AUSTRAC of Australia and MAS of Singapore needs companies to pay more attention to risk-based obligations and group-wide controls across branches and affiliates.
In the UAE, Japan, India, and Brazil, regulators need ongoing monitoring and risk profiling. These regulatory bodies show our readers the global expectation that institutions have ongoing, and risk-sensitive PEP screening work done.
| Country Regulator(s) | Screening Required? | EDD | Mandatory? |
| United States | FinCEN | Yes | Yes, for foreign PEPs |
| United Kingdom | FCA / JMLSG | Yes | Yes (domestic & foreign) |
| European Union | ESAs / AMLD6 | Yes | Yes |
| Singapore | MAS | Yes | Yes |
| Australia | AUSTRAC | Yes | Yes |
| Canada | FINTRAC | Yes | Yes, for foreign PEPs |
| India | RBI / SEBI | Yes | Yes, for foreign PEPs |
| UAE | CBUAE / DFSA | Yes | Yes |
| Brazil | COAF | Yes | Yes |
| South Africa | FSCA / FIC | Yes | Yes |
| Türkiye | MASAK | Yes | Yes |
What Is a PEP Database and How is It Maintained?
In a PEP database, the information of PEPs, their family members and close people are kept; these information are later used when performing PEP screening.
The PEP database has information from all around the world and is filled with facts from various sources. With doing manual curation, these databases can be kept up-to-date, but this process isn’t recommended in 2025 since it is slow and has room for fault. AI-driven automation, on the other hand, has ongoing monitoring of various sources and detects when there’s been changes in those sources.
What are the Tools for Global PEP Screening?
For this part, we’ll give more details about the tools used for PEP screening to our readers. The main thing you need to focus on comes from documentation and audit work, so we’ll give you three tips to ease your PEP screening questions. The first tip is keeping time-stamped logs; this means that you need to record every screening automatically and update for traceability accordingly. Our second this is keeping reviewer notes. Compliance officers should include more context clues during their investigation of odd situations.
Finally, escalation records are needed. You will need to track when your alerts are escalated to higher places for investigation; this helps you during the process of keeping accountability.
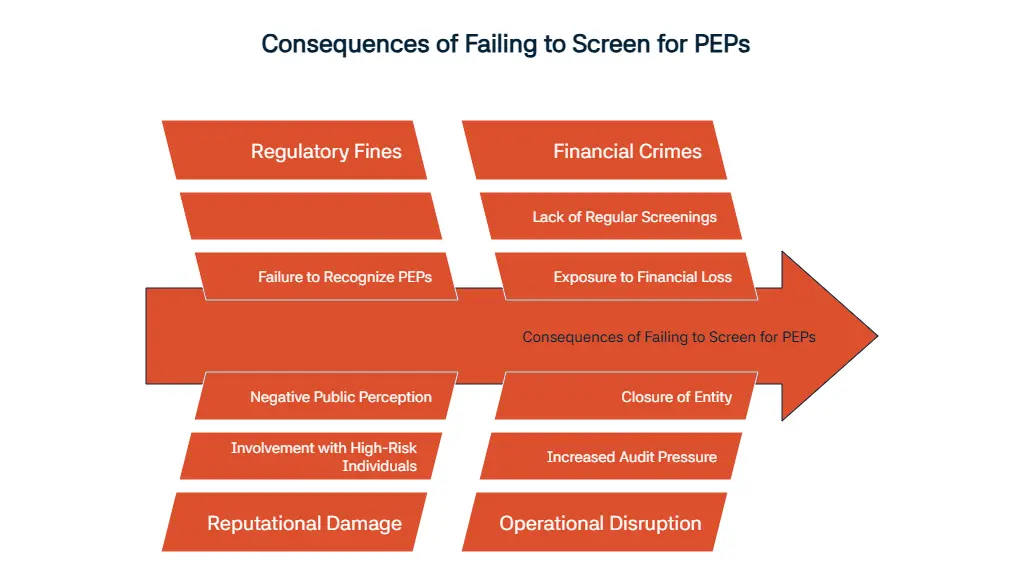
What are the Consequences of Failing to Screen for PEPs?
We’ve mentioned the benefits of PEP screening above; now, let’s talk more about the consequences you will face for not doing these screenings. The first consequence you may face is regulatory fines given to you because of failure of recognizing and profiling PEPs.
Another cost of failing to perform continuous PEP screenings is reputational damage. Your company’s reputation may get hit because of your involvement with these high-risk individuals. Finally, without having regular PEP screenings to ensure safety from PEP crimes, you are more exposed to financial crimes. This may later lead to financial loss, more fines and decreased trust.
| Consequence Type | Description |
| Regulatory Fines | Imposing financial penalties |
| License Suspension | Temporary or permanent loss of permission to operate legally |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of customer trust and damaging the brand identity |
| Criminal Liability | Legal action against compliance staff for violations |
| Increased Audit Pressure | More frequent and detailed reviews of authorities |
| Operational Disruption | Business delays, extra workload, reduced efficiency |
| Closure of Entity | Shutting down companies entirely |
How Often are PEPs Checked?
PEPs should firstly be checked during onboarding, this is to make sure you know who you are working with. Later, daily or weekly checks are essential to keep an eye on these individuals. People who are in more sensitive positions or who are riskier might require more frequent checks; the same can’t be said about lower risk customers. You should conduct screening according to the risk profile of the particular person.
Recommended PEP Screening Frequency
| Stages | Frequency | Why Is It Important? |
| Customer Onboarding | Mandatory (real-time) | To prevent onboarding high-risk individuals |
| Ongoing Monitoring | At regular intervals (daily to monthly) | To detect status changes (e.g., becoming or ending up being a PEP) |
| High-Risk Clients | Continuous (real-time alerts preferred) | Due to exposure to corruption risk |
| Periodic Reviews | Annually or based on risk profile | Reassessing client risk classification |
How can Sanction Scanner Help You Identify PEPs?
We at Sanction Scanner are ready to help you with your PEP screening needs. Our Sanction Scanner team makes sure you get the best service by first providing real-time global PEP database. At this point, you should know how important getting up-to-date database lists are for PEP screenings. We also provide a AI-powered fuzzy matching engine that detects variations, aliases, and translations. One other benefit of using Sanction Scanner is receiving continuous screening and alerts when a suspicious activity occurs.
We also provide adverse media and sanctions integration for our customers that not only provides ongoing monitoring but also combines PEP screenings with negative news and sanctions screening. Finally, our team helps you export audit logs and various more details of your screenings to help you with regulatory reporting.
FAQ's Blog Post
PEP screening is the process of checking individuals against databases to identify Politically Exposed Persons who may pose higher financial crime risks.
It helps organizations prevent money laundering, corruption, and reputational risks by monitoring high-risk clients.
A PEP is someone holding a prominent public position—such as government officials, politicians, judges, or senior executives of state-owned companies.
A PEP check compares customer data against global PEP lists, sanctions databases, and adverse media sources.
PEP checks should be done during customer onboarding and continuously through ongoing monitoring.
Failure to screen may expose businesses to money laundering, legal penalties, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Yes, relatives and close associates (RCAs) of PEPs are also considered high-risk and must be screened.
It should be continuous—organizations need to monitor customer status for changes in real time.
Advanced AML software automates PEP screening with real-time data, fuzzy matching, and risk scoring.


