AML Solutions For
Banking Industry
We help banks in the AML compliance process with our AML solutions!
TRUSTED BY OVER 800+ CLIENTS










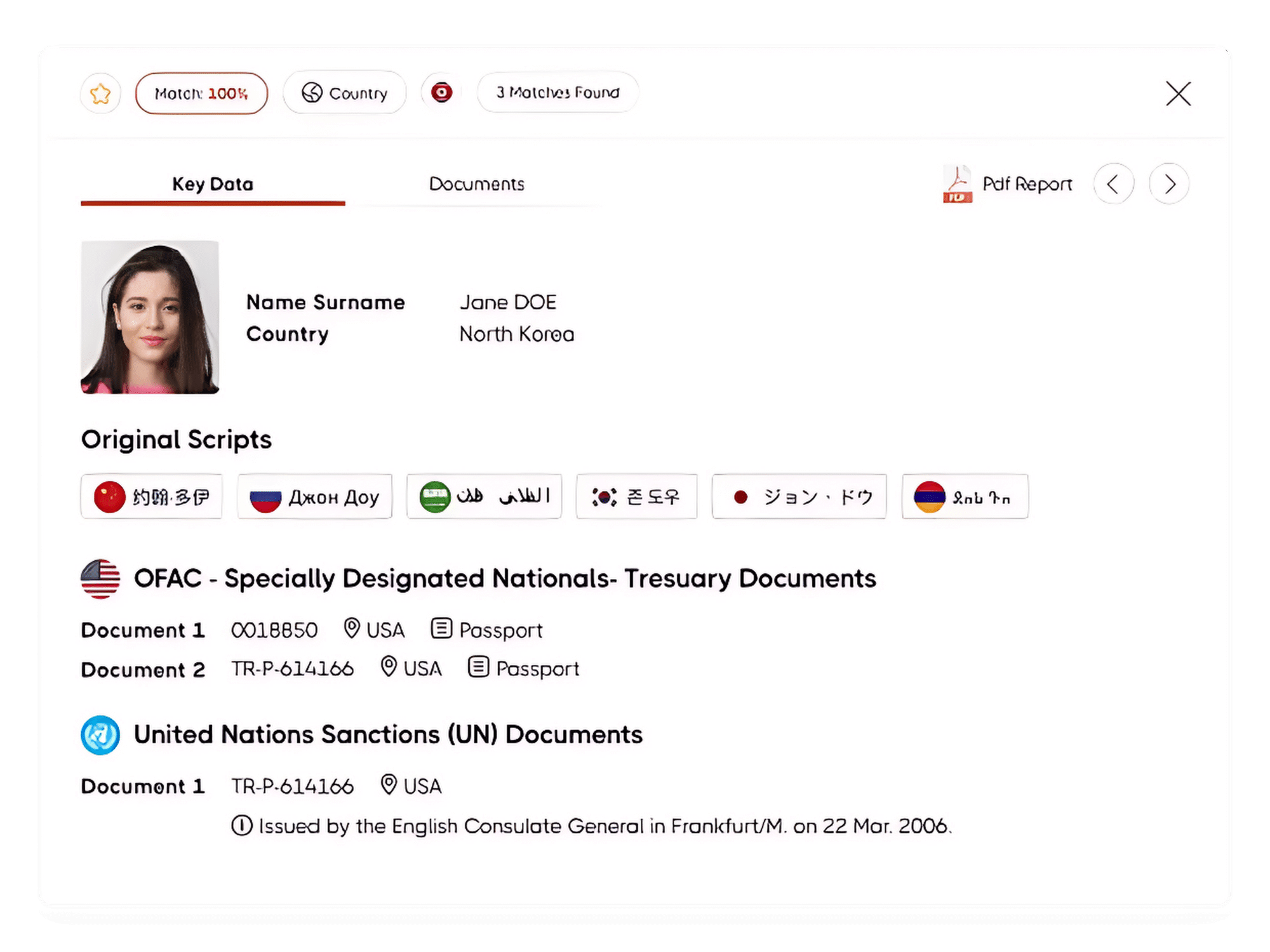
Customer Onboarding Process in Compliance
The Sanction Scanner database contains more than 3000 sanction lists, PEP lists, and adverse media data. Banks can scan their customers in seconds during the customer onboarding process using our AML Screening Software via the web or API.
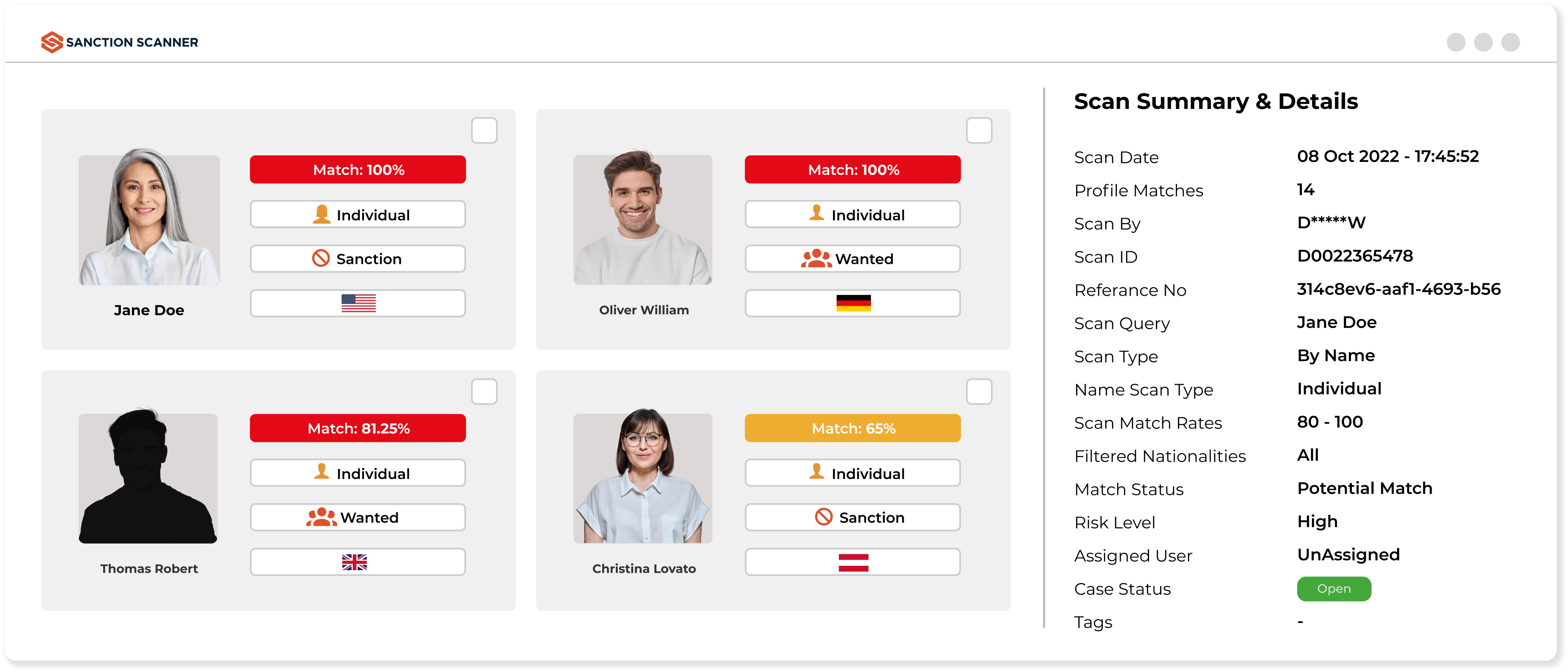
Reduce False Positives and Manual Screening
You can reduce false positives with our enhanced analytics algorithm and searching capabilities. You can see the risks customers bring, Sanctions, PEPs lists, and watchlists on one page and create reports. You can also create your safelists, localists, blacklists, special dynamic rules, and scenarios to prevent false alarms using our Transaction Monitoring Software.

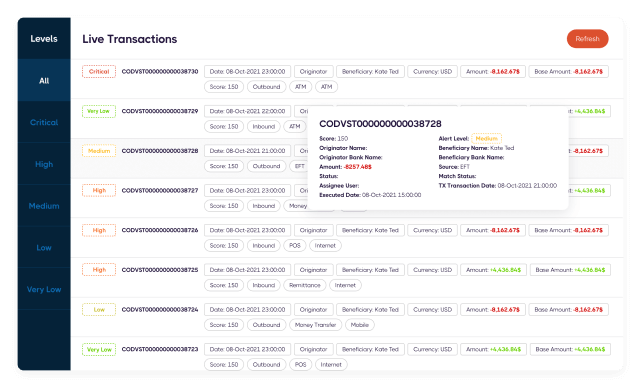
Transaction Monitoring Software for Banks
Sanction Scanner provides enhanced AML Transaction Monitoring Software. AML Transaction Monitoring Software provides end-to-end features that enable banks to meet their AML & CFT obligations. Enjoy your powered and accelerated compliance process with dynamic rules and scenarios, an advanced sandbox test environment, real-time alarms, and risk-based scorecard features.
Effortless Integration and Customized Support for Your Team
Sanction Scanner can work with APIs and Web Screens. Integrating with Sanction Scanner is very easy. We have a very detailed Restful API document and many integration options. The integration specialist of Sanction Scanner will help your business if you have trouble integrating API to your project.
Featured news and press releases
FAQs about Banking
AML Banks must apply policies, conduct KYC, monitor transactions, report suspicious activity (SAR), and screen against sanctions lists to meet regulatory requirements.
They use AML software to monitor transactions, screen against PEP and sanctions lists, and flag unusual behavior using machine learning and advanced analytics.
Banks must screen clients and transactions against OFAC, EU, UN, and other lists to avoid dealings with sanctioned entities. Screening is ongoing and critical to compliance.
It helps detect suspicious patterns like layering or structuring in real time, allowing banks to block illicit transactions and report them accurately.
KYC verifies identity, assesses risk, and ensures legitimacy of funds. It prevents fraud, enables due diligence, and is essential in stopping money laundering.
Examples include unusual cash activity, transfers without clear purpose, dealings with high-risk countries, and transactions inconsistent with income or profile.
By using AI, fuzzy logic, and risk scoring tools like Sanction Scanner, banks can prioritize real threats and reduce manual workload from false alerts.
Yes. Banks must file SARs to regulators like FinCEN or FCA. Non-compliance may lead to fines, license suspension, or legal action.
AML targets money laundering from crime; CFT focuses on terrorist financing. Banks must comply with both to meet financial crime prevention standards.
Effective programs use integrated tools for KYC, screening, and monitoring. Automation, audit trails, and real-time alerts ensure regulatory readiness.
A SAR is a report filed by banks to financial intelligence units when suspicious or potentially illicit activity is detected in customer accounts or transactions.
AML policies should be reviewed and updated annually or whenever there are significant regulatory changes or risk profile shifts.
Yes. Ongoing monitoring includes periodic risk reviews, sanctions screening, and updated KYC to ensure continued compliance with AML requirements.
Penalties include regulatory fines, license revocation, criminal liability, and reputational damage. Severe breaches may lead to prosecution of responsible individuals.
Banks assess risk using factors such as customer type, geography, transaction behavior, business activity, and past alerts, often via automated risk scoring models.
EDD involves deeper checks on high-risk customers, including source of funds verification, ownership structures, and ongoing monitoring for unusual behavior.
Large cash deposits, cross-border transfers, structured transactions, and deals involving high-risk jurisdictions or entities typically trigger mandatory reporting.
Yes. Fintech banks must comply with the same AML, KYC, and CFT obligations as traditional banks, including monitoring, reporting, and customer verification.
Yes. Modern AML software integrates with core banking systems via API or middleware, enabling real-time screening, transaction monitoring, and audit logging.
Regulatory bodies such as FinCEN (U.S.), FCA (U.K.), and FATF-aligned national authorities oversee AML compliance, depending on the bank�s operating region.




