In the European Union (EU), preventing money laundering and terrorist financing is a major focus. Financial institutions, like banks, have to take steps to stop these illegal activities. Knowing where money comes from and where it goes is key. The EU keeps an eye on new risks and updates its rules accordingly.
Since the first anti-money laundering rule in 1991, the EU has been updating its regulations to keep pace with changes, like the rise of virtual assets and crowdfunding. Recent rules, such as the one on tracing fund transfers, show the EU's commitment to staying on top of things.
KYC and AML Regulators in the EU
In the EU, keeping financial systems safe from money laundering and terrorist financing is a collective effort involving various regulatory bodies. The European Commission plays a pivotal role by conducting thorough risk assessments to pinpoint and address risks within the EU internal market. Additionally, the commission ensures the effective enforcement of anti-money laundering (AML) legislation by overseeing the transposition of EU laws and collaborating closely with competent authorities.
Collaboration extends to the European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs). Through a joint committee with the Commission, the ESAs issue guidelines and opinions to assist national competent authorities in understanding regulatory expectations, fostering consistency across the EU.
A significant development in the EU's AML/CFT framework is the introduction of the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA). AMLA supervises the EU’s AML/CFT efforts. AMLA's aims include enhancing cooperation among financial intelligence units (FIUs) and coordinating national authorities to ensure consistent application of EU rules within the private sector.
The European Banking Authority (EBA), established in 2011, aims to protect the financial stability of the EU banking sector. It assesses risks, develops harmonized regulations, and collaborates with the European Commission and national regulators. The EBA operates above national regulators, working to combat financial crimes and safeguard the financial system across the EU and its member states from its headquarters in France.
Current KYC and AML Regulations in the EU
Recent years have seen the introduction of stricter financial regulations aimed at bolstering enforcement powers across the EU. This drive for stronger regulation was highlighted in the European Commission's Action Plan (May 2020), signaling a concerted effort to combat money laundering and terrorist financing effectively. Since then, several regulations entered into force in cooperation with the FIUs.
Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD)
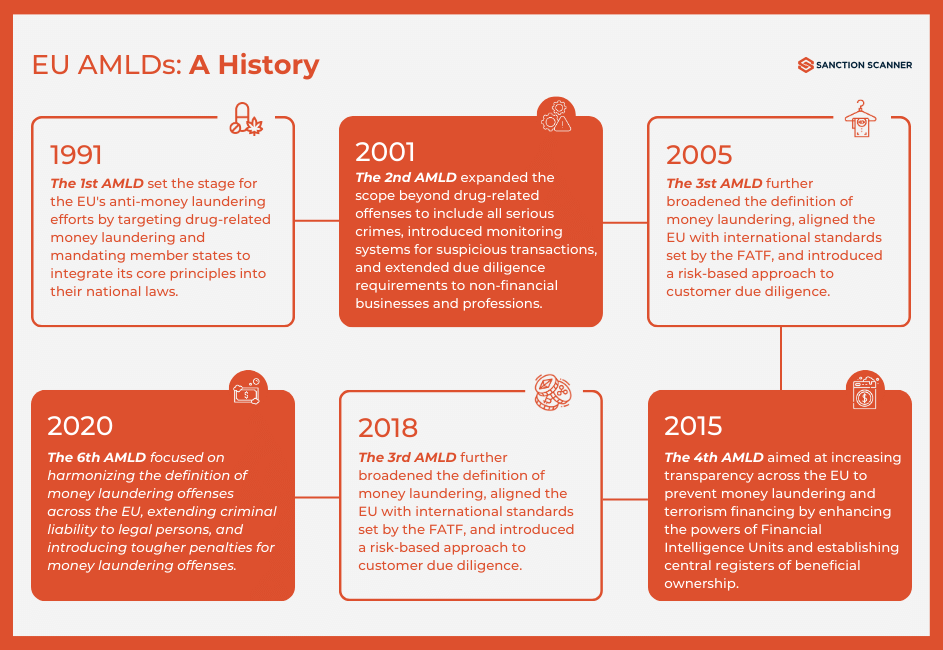
The 6AMLD stands as a pivotal step forward in the European Union's efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. Enacted in October 2018 and activated on December 3, 2020, this directive represents a significant enhancement of the EU's regulatory framework. Building upon the foundation laid by previous directives, notably the Fourth and Fifth AML Directives, the 6AMLD introduces robust criminal legislation aimed at strengthening the EU's capacity to address financial crimes effectively.
These provisions include standardized definitions of money laundering offenses, the extension of criminal liability to legal entities, and the imposition of fines, sanctions, and potential exclusion from public aid and judicial procedure on offenders. Additionally, the directive addresses emerging challenges, such as virtual currencies, by establishing uniform guidelines for investigative tools and jurisdictional determinations.
Market Abuse Directive/Regulation (MAD/MAR)
The MAD and subsequent MAR are pivotal in upholding the integrity of European financial markets and bolstering investor trust. Market abuse, encompassing insider dealing, unauthorized disclosure of inside information, and market manipulation, is strictly prohibited under these regulations.
MAR's objective is to foster efficient and transparent European financial markets while leveling the playing field for economic operators across member states. Unlike MAD, MAR extends its jurisdiction to various trading platforms, including Multilateral Trading Facilities (MTFs) and Organised Trading Facilities (OTFs), along with emission allowances. It empowers national competent authorities with supervisory and investigatory powers and a framework of administrative sanctions to combat market abuse effectively.
Published in 2003, MAD laid the foundation, while MAR represents a comprehensive update reflecting evolving market dynamics.
Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2)
Proposed in 2013 as an amendment to PSD, PSD2 aims to fortify consumer protection, foster competition and innovation, and enhance security within the payments market. Notable changes include the opening of banks' payment services to Third Party Payment Services Providers (TPPs), prompting significant industry upheaval.
PSD2 regulates and harmonizes two key services: Payment Initiation Services (PIS) and Account Information Services (AIS). AIS consolidates information from various bank accounts, offering consumers a comprehensive view of their finances. PIS enables online payments via banking interfaces, streamlining transactions between consumers and merchants.
PSD2 also introduces Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), mandating two-factor authentication for online banking operations. This enhances security by requiring additional authentication factors beyond traditional card information. These changes aim to promote competition, innovation, and security while ensuring compliance among all payment service providers, traditional and new alike.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR serves as a comprehensive framework aimed at safeguarding the personal data of individuals within the EU. Its core objective is to empower individuals by granting them control over their personal information while imposing stringent obligations on organizations handling such data.
Under the GDPR, organizations must establish a lawful basis for collecting, processing, and storing personal data, ensuring transparency regarding the purposes for which data is used. Explicit consent from individuals is mandatory for data collection, processing, and storage, with provisions for data deletion when no longer necessary.
Moreover, the GDPR delineates various rights for individuals, including access to their data, the right to data deletion, and the ability to rectify inaccuracies. Compliance entails demonstrating adherence to GDPR standards, with significant penalties for non-compliance.
Considerations for EU Regulations: Due Diligence
Reaching the requirements set by the 6AMLD is vital for each company and individual operating in the EU. Compliance with the MAD/MAR necessitates vigilance in detecting and reporting market abuse activities. Understanding and implementing the provisions of PSD2 and GDPR are crucial for seamless operations.
The EU's requirements include thorough consideration and proactive measures. Adherence to AML and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations demands robust measures in Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD).
To navigate these regulations effectively, a deep understanding of these measures, together with compliance strategies, is imperative. Collaboration with regulatory bodies and continuous monitoring of regulatory updates are essential for sustainable compliance in the EU.
Innovative Solutions for CDD and EDD Measures
Establishing robust CDD processes involves:
- Verifying the identity of customers,
- Assessing their risk profiles,
- Monitoring transactions for suspicious activities, etc.
Additionally, implementing EDD measures, such as enhanced scrutiny of high-risk customers and transactions, further strengthens AML efforts and mitigates potential risks.
Such procedures are recommended to be made through innovations presented by the innovative software to align companies and individuals better to today's fast-paced world.
Sanction Scanner provides robust CDD and EDD measures in their numerous tools, all crafted meticulously to ensure security and stability for your company's and your own well-being. Contact us or request a demo today to learn more about these state-of-the-art tools.




