What is Regulation?
Regulations are formal authorities or special corporation-made rules to manipulate actions in precise areas like finance, fitness, or environmental safety. They're not continually laws however act beneath the pressure of law and help put into effect extra popular statutes. According to our experts, rules form the backbone of any successful society-they ensure that legal guidelines aren't simply symbolic however actionable in actual lifestyles. Without rules, the bulk of legal guidelines would be ambiguous or vain.
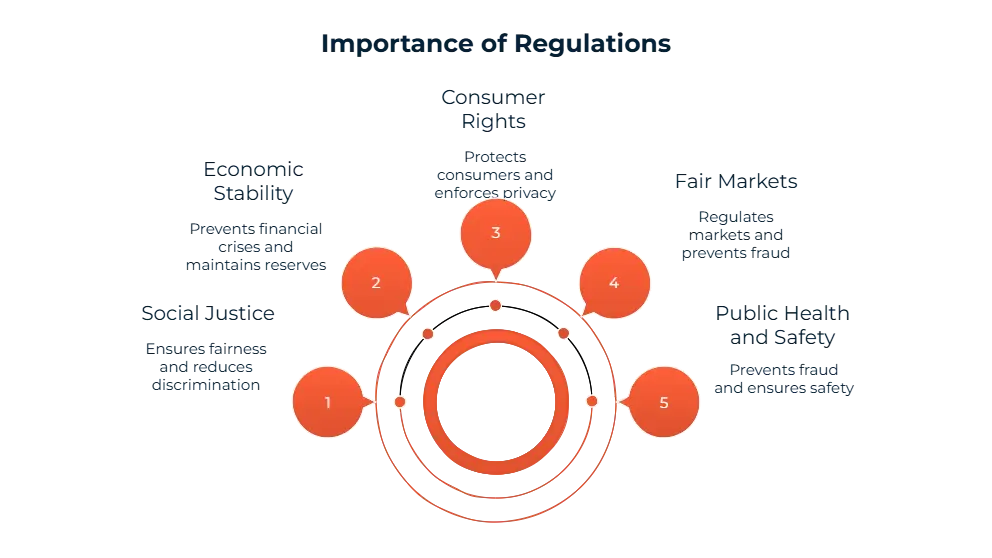
Why Are Regulations So Important?
Protecting Public Health and Safety: Regulation of finance brings about a degree playing subject and stops fraud.
Ensuring Fair Markets: The SEC, as an example, regulates securities markets and sanctions insider buying and selling. In 2022 by itself, SEC enforcement movements recovered over $6 billion for cheated investors.
Safeguarding Consumer Rights: Consumer safety laws perform to offer product safety and non-discrimination in remedy. A extremely good working example is the EU's GDPR, whose governance of records privacy has substantially boosted enforcement and penalized violators over €1.5 billion up to now.
Promoting Economic Stability: Regulatory mechanisms like Basel III mandate banks to maintain enough reserves, which act to avoid a repeat of the 2008 monetary crisis. This law isn't red tape for pink tape's sake—it's an financial stabilizer.
Upholding Social Justice: Legislation like the Equal Pay Act and OSHA administrative center guidelines guarantees people' rights and decreases discrimination. We assume that this sort of regulation is crucial to constructing a fairer, extra balanced work environment.
How Are Regulations Made?
Making a law normally entails the subsequent steps:
1) Legislation Passed: A regulation is first passed with the aid of a legislative frame, granting authority to behave on a selected trouble.
2) Delegation to Specialized Agencies: Such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or FDA is also referred to as upon to draft and enforce unique rules inside the context of the regulation.
3) Rulemaking Process
• Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM): A proposed rule is published.
• Public Comment: Public, experts, and stakeholders provide comments.
• Final Rule: The revisions are made according to feedback and the regulation becomes effective.
Once completed, the regulation is implemented by means of inspections, fines, or legal proceedings for non-compliance. According to our experts, the incorporation of public opinion is what makes the process more democratic, although it doesn't always ensure that all voices are heard to the same degree.
Which Industries Are Subject to Regulations?
• Healthcare: Ensures patient safety and ethical medical practices.
• Financial: Regulated to maintain market integrity and prevent fraud.
• Energy: Adheres to guidelines for sustainable practices.
• Manufacturing: Monitored to ensure quality standards.
• Telecommunications: Regulated for quality standards.
• Food production: Ensures consumer safety.
Regulation vs. Law: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Law | Regulation |
| Created by | Legislature | Government agency |
| Scope | Broad and principle-based | Specific and detail-oriented |
| Change Process | Requires parliamentary action | Can be updated administratively |
| Enforced by | Courts | Agencies (with legal authority if necessary) |
What Are the Types of Regulations?
There are 5 main types of regulations. Purposes and examples could define the importance and features.
| Type | Purpose | Example |
| Financial Regulations | Prevent fraud and ensure market integrity | SEC Rules, Basel III |
| Environmental Regulations | Preserve nature and reduce pollution | Clean Air Act, Paris Agreement |
| Health & Safety Regulations | Protect people in workplaces and healthcare | FDA Drug Approvals, OSHA guidelines |
| Consumer Protection | Safeguard buyer rights and privacy | GDPR, Fair Credit Reporting Act |
| Trade and Commerce | Manage global trade and fair competition | WTO Rules, Antitrust Regulations |
What Are the Regulatory Agencies?
Here, you can see the most important regulatory bodies all around the world. These agencies have own focus areas for different industries. These regulators from different countries protect the markets.
| Acronym | Full Name | Country | Focus Area |
| SEC | U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission | USA | Financial markets |
| EPA | U.S. Environmental Protection Agency | USA | Environmental protection |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration | USA | Food and pharmaceuticals |
| FCA | Financial Conduct Authority | UK | Financial services |
| ESMA | European Securities and Markets Authority | EU | Securities markets |
| ASIC | Australian Securities and Investments Commission | Australia | Investments and corporate law |
| OFR | Office of Financial Research | USA | Financial research and risk analysis |
| CFTC | Commodity Futures Trading Commission | USA | Commodities and derivatives markets |
| FINRA | Financial Industry Regulatory Authority | USA | Brokerage firms and exchange markets |
| BaFin | Federal Financial Supervisory Authority | Germany | Financial institutions and markets |
| AMF | Autorité des marchés financiers | France | Financial markets regulation |
| CNMV | Comisión Nacional del Mercado de Valores | Spain | Securities markets |
| MAS | Monetary Authority of Singapore | Singapore | Financial services and monetary policy |
| SFC | Securities and Futures Commission | Hong Kong | Securities and futures markets |
| FSS | Financial Supervisory Service | South Korea | Financial supervision and regulation |
| FSCA | Financial Sector Conduct Authority | South Africa | Financial sector conduct authority |
| CBIRC | China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission | China | Banking and insurance |
| FSSAI | Food Safety and Standards Authority of India | India | Food safety and standards |
Landmark Regulations in Action
Dodd-Frank Act (USA): Created after the 2008 disaster, Dodd-Frank positioned stricter controls on banks and set up oversight bodies like the CFPB to guard consumers.
GDPR (EU): This statistics privateness regulation revolutionized how agencies manage person statistics. From our attitude, it’s a effective tool that forces organizations to take privateness severely.
OSHA Standards (USA): OSHA guarantees workers are not uncovered to pointless risks. These regulations were important in decreasing place of business injuries and deaths, particularly in dangerous industries.
FATF Recommendations (Global): The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets global standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. These recommendations form the backbone of AML laws in over 200 jurisdictions.
What Are the Effects of Regulations?
There are huge effects of regulations because of the rules in these industries.
| Impact on Individuals | Impact on Businesses |
| Safer goods, cleaner environments | Higher compliance expenses and extra documentation |
| Greater data privacy | Increased transparency and inner responsibility |
| Safer workplaces | Need for schooling, audits, and machine improvements |
A greater regulated enterprise may also face better charges prematurely, but it regularly builds better consider and long-term value.
What Are the Regulations in the Banking Sector in Terms of AML?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies are key to preventing monetary crime. Banks are required to:, verify purchaser identities (Customer Due Diligence), monitor transactions for suspicious conduct, report massive or unusual activities and maintain enormous financial statistics.
FAQ's Blog Post
A regulation is an official rule issued by a government agency that explains how a law should be applied in daily practice. It ensures consistency, safety, and fairness across industries by providing detailed instructions for legal compliance.
Regulations are created by government agencies such as the EPA or SEC. These agencies are authorized by legislative acts to write and enforce rules within their area of expertise, translating broad laws into actionable, enforceable guidelines.
Yes, regulations have the force of law. Once issued by an authorized agency, they must be followed just like any other legal requirement. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, or legal action depending on the regulation's scope.
Judges can hear them if they're viewed as unconstitutional, too ambiguous, or beyond the authority of the agency.
Bank regulation involves the rules and oversight established by governments to ensure banks operate securely, manage risk, and comply with financial laws. It aims to protect consumers, promote market stability, and prevent crimes like money laundering.
Regulation refers to the rules and laws that banks must follow. Supervision is the ongoing monitoring and enforcement of those rules by regulatory authorities. In short: Regulation = rule-making Supervision = rule-enforcing
Regulation is a set of authoritative rules issued by a government or regulatory body to control behavior in a specific sector. These rules are designed to protect the public, ensure fairness, and maintain order in business and industry practices.



