What Is Identity Theft?
In this blog post, we’ll be explaining what identity theft and identity fraud are. We’ll give you the details of these crimes and further explain the differences between the two.
Identity theft is done with criminals stealing a person’s personal information like their Social Security number, identification details, date of birth or more and using them without permission or knowledge of the person. Our readers might be wondering. How do criminals get a hold of this information? These people use phishing scams, data breaches, or social engineering tactics that are made to convince people to reveal sensitive details. After they steal your information, they use these details as the first step in their fraud chain. Further steps involve financial fraud, credit card fraud, or impersonation to trick companies.
What Is Identity Fraud?
Identity fraud is done with criminals using stolen or synthetic identities like fake profiles that are created with a combination of real and fake information to commit financial crimes. With these information, they can commit credit, insurance, or government fraud. What we mean by these is that they might apply for things like credit cards or loans, file false insurance claims, or exploit government programs, which are otherwise used to encourage consumers, for their financial gain.
Identity Theft vs Identity Fraud: What’s the Difference?
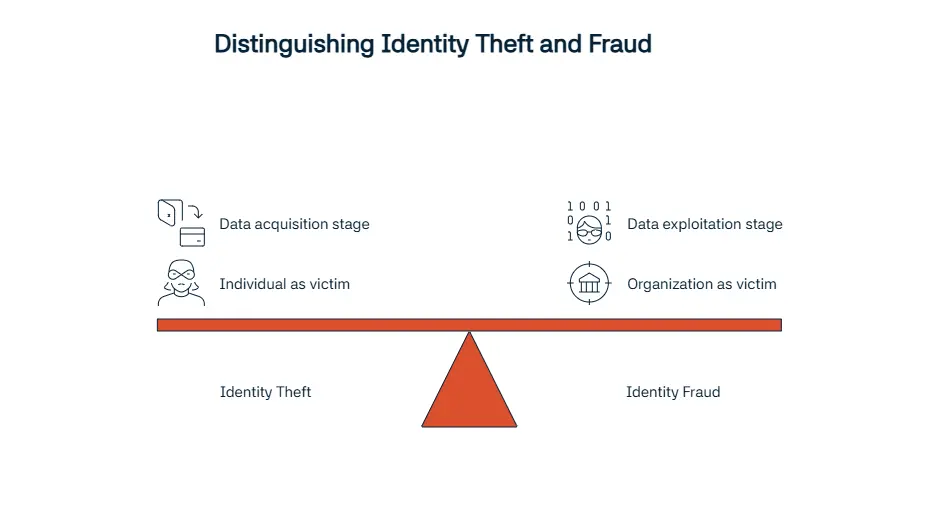
These two crimes might look and sound the same and might be used for describing the other, but make no mistake, they are different terms. Identity theft is used when talking about the act of stealing personal information. However, identity fraud is the next step after getting a hold of these information. Criminals use stolen personal details or synthetic IDs that are created by using your personal information to commit identity fraud. Some examples for identity fraud are financial scams, insurance fraud, or government programs abuse.
Theft is done to obtain the data, while fraud is done to exploit the said data to use it for gain. Our team at Sanction Scanner advises you get ahead of any loss you may face by preventing identity theft before it occurs. In the UK, in fraud cases, the individual or company e.g., your bank who has or may have suffered a financial loss through the use of the stolen identity, will be the person considered the victim of fraud and you will be considered as a victim of identity theft.
What Are the Common Types of Identity Fraud?
Identity fraud has many types since fraudsters are looking to commit crimes of all kinds. One of the most common types of identity fraud is account takeover. This type of fraud is done by taking control of an existing bank account to steal the funds inside the account. Another example is credit card fraud, where fraudsters will either get new cards in your name or use your already stolen card for purchases.
One other tactic is synthetic identity fraud. This is done by using real information of a person and mixing is with fake details; this process creates a new identity that is convincing to officials. Another way these fraudsters use is medical and benefits fraud. They use the identities they stole to get healthcare services, medicine, or government assistance.
What Are the Red Flags of Identity Fraud?
There are many indicators for identity fraud and spotting them earlier will help save you from dealing with damage. Login anomalies are the first red flag to watch out for. If you’re sure you’re not the one that tried to login many times unsuccessfully, from an unknown location, or in odd times, you might be dealing with identity fraud. One other indicator is document mismatch. In this situation, the information and records provided by the fraudster is inconsistent with official information.
Another thing to watch out for is suspicious transactions. Transactions of high amount, withdrawals that seem suspicious since they aren’t explained, and changes in spending patterns may indicate identity fraud. Device or location issues are also another red flag. Some examples are logins from different places in a rapid pace, and multiple accounts being handled from one device.
Which Institutions Are Vulnerable to Identity Fraud?
Banks, fintech firms, and cryptocurrency platforms are especially under risk when it comes to identity fraud. These firms are dealing with financial transactions which makes them more vulnerable to fraud. Fintechs and Banking-as-a-Service platforms were identified by RUSI as especially vulnerable, with BaaS providers accounting for 10% of tracked suspicious transfers.
Insurance companies and government portals are another example for companies you need to be extra careful about. With the stolen identity information, these companies can be used to commit benefits fraud or file false claims. In 2024, there were more than 1.1 million reports of identity theft received according to the FTC’s IdentityTheft.gov website. This data shows that many of these stolen information can be used to further scam people.
What Regulations Address Identity Theft and Fraud?
Identity theft and identity fraud are serious crimes that consumers need protection from; therefore, there are several regulatory bodies and regulations that deal with these issues. The first example we’ll give is Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Recommendations 10-12 which figure out standards for CDD, PEP monitoring, record keeping, and are essential in preventing identity fraud.
In the EU, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets forth regulations that protects personal data and ensures there are strict requirements for companies to comply with during the process of collecting and saving personal information.
In the U.S., the Identity Theft and Assumption Deterrence Act of 1998 declared identity theft as a federal crime. This move by them helped Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and other regulatory bodies while implementing measures against fraudsters. Similarly, the UK National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) is there for guidance in the process of companies enforcing safe measures against identity fraud. In India, the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) regulates the Aadhaar system to make sure these personal informations are used responsibly.
How Can Companies Detect and Prevent Identity Fraud?
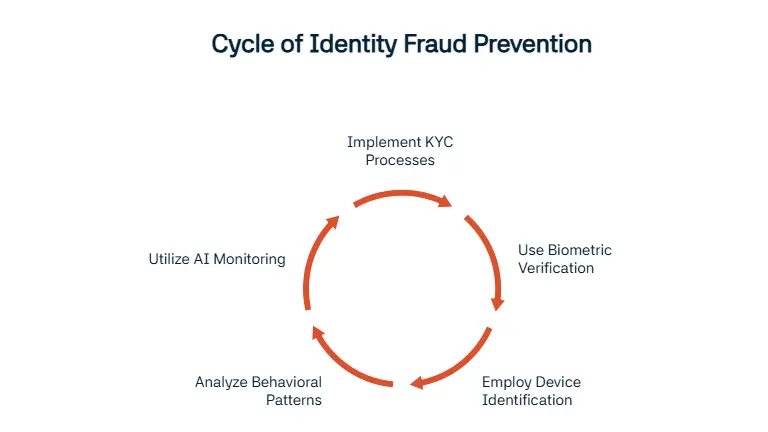
For those who are looking to prevent identity fraud from happening, we will be giving some advices for detecting. The first action companies can take is implementing Know Your Customes (KYC) processes that help verify users through official information. Biometric verification is a new technique that is used by companies, it helps provide extra protection. Device identification and behavioural analytics is also important for companies. Logins from the same device is a normal action whereas constant logins from devices that are not recognized is something that companies should watch out for. Unknown login locations and strange transactions patterns are also recognized by behavioural analytics.
AI based monitoring systems are getting more popular every day; these systems use the power of AI to work more efficiently and safely. An AI based system can also monitor huge amounts of information continuously.
What Role Do RegTech Tools Play?
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) tools are essential for protecting yourself against identity fraud; these tools are equipped to help your company. These tools provide real time alerts that help companies figure out odd activities right away and respond quickly. These tools also use risk scoting models to identify customers with risky details, transactions, and behaviours.
Another feature we’ll mention is sanctions and politically exposed persons (PEPs) screening. These screenings figure out if there is a customer of yours who is in global sanction watchlists, or is a high-risk individual. Tools provided by Sanction Scanner provide these features and many more to help companies reach compliance and protect themselves against fraud.
What Should Victims of Identity Theft Do?
If you’re ever a victim of identity fraud, the first thing you should do is reporting the incident to the authorities, like filing a police report. This will start the process of catching the fraudster. Afterwards, you should place a credit freeze which prevents fraudsters from opening new accounts with your information. You can prevent financial loss this way. After completing these steps, setting up a fraud alert can help other providers pay extra attention while verifying customers. Identity theft is no joke and you can protect yourself with these steps.
How to Report Identity Fraud or Theft?
After finding yourselves in a situation of identity theft or identity fraud, your next step should be reporting these incidents. In the U.S., you can report identity fraud and identity theft to identitytheft.gov. The address for reporting in the UK is actionfraud.police.uk. Finally, in India, you can go to cybercrime.gov.in to report these crimes.
How Sanction Scanner Helps Prevent Identity Fraud
We at Sanction Scanner help you prevent identity fraud by identity scoring. This step helps you by dividing customers by their risk score that is figured out by checking their information against sanction lists, and adverse media.
We perform real time checks; these checks flag suspicious activity that occur during transactions. Another way Sanction Scanner helps is by implementing KYC and KYB measures to your systems. These measures will help you verify companies against official information. Another feature of Sanction Scanner is behavioural monitoring; this feature provides a tracking of user activity patterns to detect if something odd happens.
FAQ's Blog Post
Identity theft happens when someone steals your personal information to impersonate you.
Identity fraud is when stolen information is used to commit crimes like opening accounts or making purchases.
Identity theft is the act of stealing data, while identity fraud is using that data to commit a crime.
Criminals steal personal data through phishing, hacking, social engineering, or document theft.
Victims often see unfamiliar charges, new credit lines, or suspicious account activity.
People can protect themselves with strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and regular credit checks.


