Today, the ability to transfer money across borders quickly and securely is important. Whether you are a business owner dealing with international clients or an individual sending money to family overseas, understanding the mechanisms that facilitate these transactions is crucial. Two key components in this process are SWIFT and BIC codes. But what exactly are these codes, and why are they so important?
A SWIFT code, also known as a BIC (Bank Identifier Code), is a unique identifier used by banks and financial institutions around the world. These codes are essential for ensuring that international transactions are processed accurately and efficiently. Without them, sending or receiving money across borders would be a much more complicated and error-prone process.
What is a SWIFT Code or BIC Code?
A SWIFT code, also known as a Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication Code, is a unique identifier used by banks and financial institutions globally to facilitate international transactions. This code ensures that money sent from one bank to another across borders reaches the correct destination without any hitches. Essentially, a SWIFT code acts like an international bank address, guiding the transaction to the right place.
Is there a distinction to be made between a SWIFT code and a BIC? The short answer is no.
Both names are commonly used interchangeably to mean the same thing. As a result, different financial organizations and banks simply brand them with different names.
It's also worth mentioning that these codes go by several names, such as SWIFT identifiers and SWIFT IDs. In practice, however, there is no discernible distinction between these names.
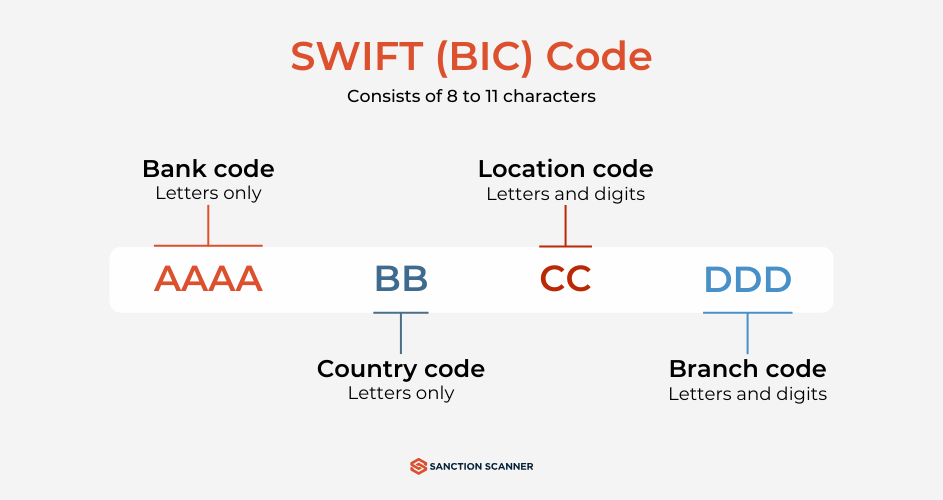
What do SWIFT Codes Look Like?
A SWIFT code typically consists of 8 to 11 characters, each segment providing specific information about the bank and its location. Here's a breakdown of the structure:
- Bank Code (4 characters): The first four letters represent the bank's name. For example, "HSBC" for HSBC Bank.
- Country Code (2 characters): The next two letters indicate the country where the bank is located. For instance, "US" for the United States or "GB" for the United Kingdom.
- Location Code (2 characters): These two characters can be letters or numbers and specify the bank's head office location within the country.
- Branch Code (3 characters, optional): The last three characters are optional and denote a specific branch of the bank. If omitted, it usually refers to the bank's primary office.
Example of a SWIFT Code
Let's take an example to illustrate a SWIFT code: HSBCUS33XXX
- HSBC: Bank Code
- US: Country Code
- 33: Location Code
- XXX: Branch Code (optional, indicating the main office)
How do SWIFT Codes Operate?
1. Initiating the Transaction
When you start an international transaction, you provide your bank with the recipient's SWIFT code. This code identifies the recipient's bank and ensures the funds are directed correctly.
2. Message Creation
Your bank creates a SWIFT message containing transaction details like the amount, currency, and account information, formatted according to SWIFT standards.
3. Secure Transmission
The SWIFT message is securely transmitted through the SWIFT network, an encrypted messaging system used globally by banks to ensure safe and accurate communication.
4. Routing the Transaction
The recipient's bank receives the SWIFT message and uses the SWIFT code to identify the specific branch and account for the funds. The code acts as a precise address for the transaction.
5. Processing and Settlement
The recipient's bank processes the transaction, verifies details, converts currency if needed, and credits the recipient's account. Intermediary banks may be involved for currency conversions or regulatory reasons.
6. Confirmation and Notification
Both the sender and recipient are notified once the transaction is complete. The sender's bank confirms the transfer, and the recipient's bank informs the recipient that the funds have been credited.
How to Find Your Bank's SWIFT or BIC Code
Finding your bank's SWIFT or BIC code is essential for international transactions. Here are quick ways to locate it:
- Log in to your online banking account and check the section for international transfers or account details.
- Look at your bank statements, either paper or electronic, where the SWIFT/BIC code is often listed.
- Visit your bank's website and search for the SWIFT or BIC code in the international banking or customer support sections.
- Call your bank's customer service for the SWIFT or BIC code.
- Use the SWIFT organization's online directory to look up your bank's code.
- Check your bank's mobile app under international transfers or account details.
- Visit your local bank branch and ask for the SWIFT or BIC code.
The Role of SWIFT and BIC Codes in International Transactions
SWIFT and BIC codes are crucial for international transactions. Here's why:
- Accurate Routing: These codes ensure that funds are directed to the correct bank and branch, minimizing errors
- Speed: SWIFT and BIC codes facilitate faster processing of cross-border payments, making transactions more efficient.
- Security: Using these codes adds a layer of security, reducing the risk of fraud and misrouting.
- Standardization: These codes provide a universal standard recognized by banks worldwide, simplifying global financial operations.
Security and SWIFT/BIC Codes
SWIFT and BIC codes play a vital role in ensuring the security of international transactions. Here’s how they contribute to a safer banking environment:
- Encrypted Communication: The SWIFT network uses advanced encryption to protect transaction details, ensuring that sensitive information is securely transmitted between banks.
- Unique Identification: Each SWIFT/BIC code uniquely identifies a specific bank and branch, reducing the risk of funds being sent to the wrong institution.
- Fraud Prevention: By providing a standardized method for identifying banks, SWIFT and BIC codes help prevent fraudulent activities and unauthorized transactions.
- Verification: Banks use SWIFT and BIC codes to verify the legitimacy of the receiving institution before processing a transaction, adding an extra layer of security.
- Compliance: SWIFT and BIC codes help banks comply with international regulations and anti-money laundering (AML) laws, ensuring that transactions are legitimate and traceable.
Enhancing Security with Sanction Scanner
While SWIFT and BIC codes are crucial for secure international transactions, it is equally important to have robust systems in place for transaction monitoring and fraud detection. This is where the Sanction Scanner comes into play. Sanction Scanner offers advanced solutions for real-time transaction monitoring and comprehensive fraud detection, helping financial institutions comply with international regulations and prevent illicit activities.
By integrating Sanction Scanner into your banking operations, you can enhance the security and efficiency of your transactions, ensuring that your financial activities are both compliant and secure.
To see how Sanction Scanner can benefit your organization, request a demo today and explore our products.




